제1회 딥러닝 컨퍼런스 2017 2일차
주최 : 서형석 대표 @ 딥러닝그룹
1. Up and Running with Tensorflow : 박규병 카카오 브레인 연구원
Up and running with Tensorflow
tensorflow-exercises
We will Cover
- basic usage of Tensorflow.
- the most important functions, focusing on the comparison with NumPy.
- programming a simple regression task with Tensorflow.
- some of basic neural network theories.
We will NOT cover
- how to install Tensorflow.
- deep understanding of deep learning.
- serious implementation with real problems
Requirements - Basic familiarity with Python and NumPy
- Bring your own laptop where Tensorflow, NumPy, and IPython have been installed.
- Deep learning background will be more than welcome, but not required.
주요 연구분야 및 관심사
Tutorials
Deep learning을 다루면서 맞닥트리는 요소들
- Mathematical background (statistics, probabilities, linear algebra)
- NN Theories (Back-propagation, activation, normalization…)
- Speed of progression
- 너무 빠르게 기술이 발전하고 있는 분야라는 것은 부담스럽다.
- Programming skills (Python, NumPy, TensorFlow, Theano…)
- English (lecture listening, paper reading, reference…)
Money (GPUs)
제대로 deep learning을 할 수 있는 역량을 기르려면
6개월 정도는 머리 싸매고 고생한다고 생각해야 제대로 어느 정도 다룰 수 있는 역량에 도달할 수 있다고 생각해야 한다.
basic terms @ TensorFlow
- TensorFlow is a programming system in which you represent computations as
graphs. - Nodes in the graph are called
Ops(abbr. for operations) - An
op takes zero or more Tensors, performs computations and produces zero or more Tensors. - a
Tensoris a typedmulti-dimensionalarray. - a
TensorFlow graphis adescription of computations. - a
graphMUST be launched in asession, then put intodevices, such asCPUs or GPUs. - these methods return tensors produced by ops as
numpy.ndarrays. - you can think of a
tensoras ann-dimension array,
Tips
- 단순한 예제를 따라하는 데 있어서는 세부적인 tensorflow사용법이 중요하지 않을 수 있다. 하지만, 깊게 deep learning 알고리즘을 적용한다면 이런 기초가 매우 필수적이다.
- 실제적인 product를 만들려고 한다면 jupyter를 사용하지 않고, IDE를 사용하는 것을 추천합니다. 생각보다 프로그램을 돌리기에 버그도 많고, 디버깅이 쉽지 않다.
기본적으로 np.array를 쓸 때는 dtype을 명확하게 명시해 주는 습관을 주는 것이 좋다.
12345# Good examplex = np.array([1,2], dtype=np.int64)# Bad exampley = np.array([1,2])tensor를 다루면서 가장 중요한 개념 중 하나가 shape, dtype이다. 제대로 된 결과가 나오는 지를 알기 위해서 값보다는 위의 두 속성들을 유심히 살펴보자.
12345_x = [[1,2], [3,4]]x = tf.convert_to_tensor(_x)print(x)# Tensor("Const_3:0", shape=(2, 2), dtype=int32)
2. Deep learning and Speech recognition - 육동석 : 교려대학교
History of AI, especially neural networks
Neural Network의 태동기 (1950s)
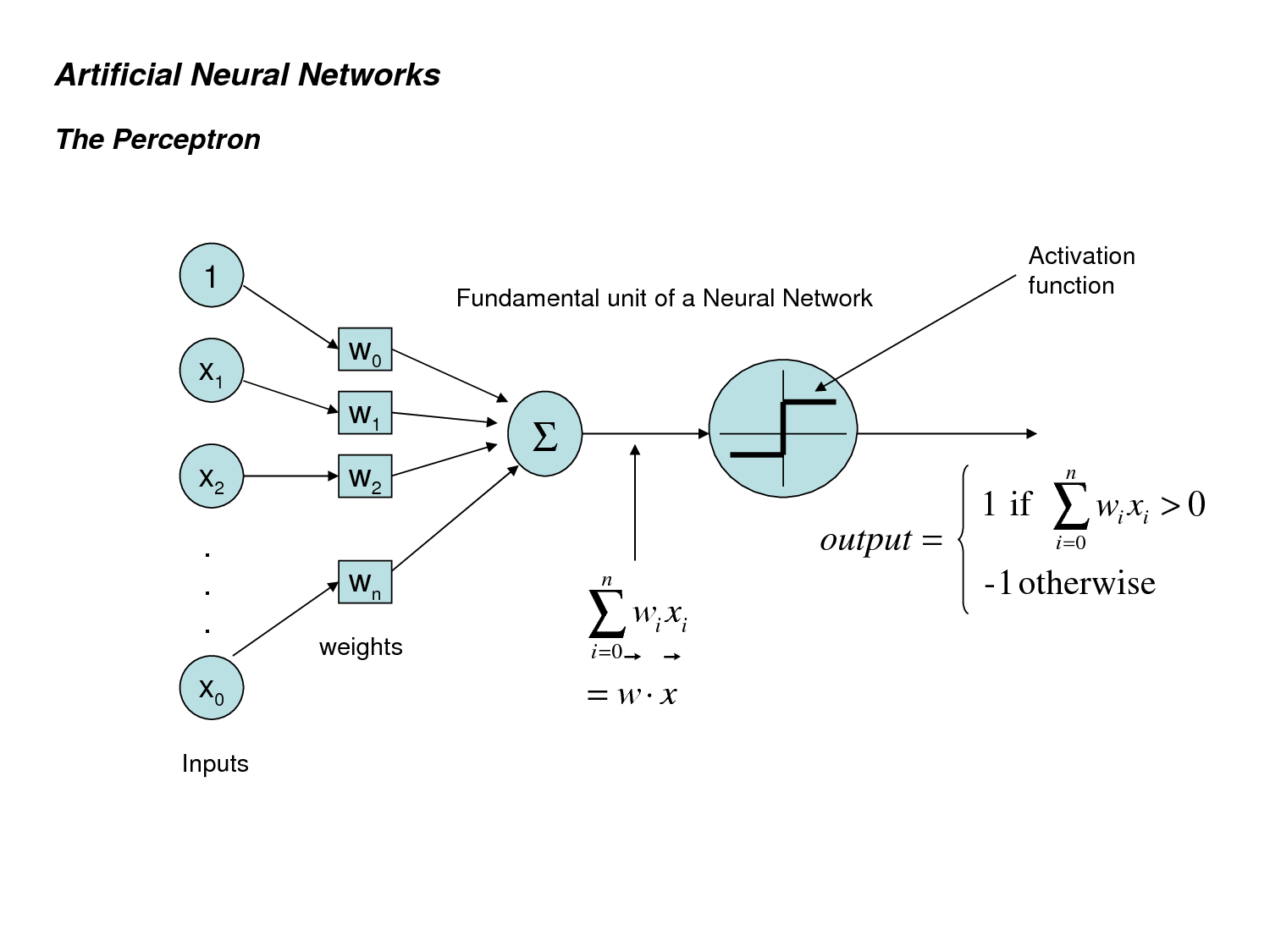
- The Perceptron: A Probabilistic Model For Information Storage And Organization In The Brain, Rosenblatt, 1958
- Perceptron이 처음으로 소개되었으며, 인간의 뇌와 비슷한 뉴런구조에 기반한 패턴인식 알고리즘가 소개되고 발전됨
Neural Network의 침체기 (1960~70s)
- An Introduction to Computational Geometry, Minsky & Papert, 1969
- 낮은 성능과 당시의 컴퓨팅 파워로는 제대로 된 계산이 불가능함을 깨달음

Neural Network의 제2번성기 (1980s)
- Parallel Distributed Processing: Explorations in the Microstructure of Cognition, Rumelhart, 1986
- Back-propagation을 통한 neural network의 성능 개선

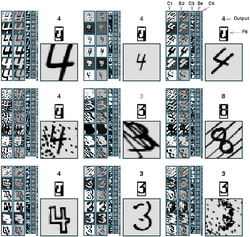
- Gradient-based learning applied to document recognition, Lecun, 1989
- MNIST 문제의 해결을 CNN이라는 개념을 처음 도입하여 해결
Neural Network의 제2침체기 (1990s)
- 별다른 발전 없이 SVM를 포함한 다른 machine learning들에 비해 발전이 더뎠음
Neural Network의 최대 번성기 : Neural Network의 재발견과 Deep learning의 발전 (2000s ~ )
- Contrastive divergence learning, Hinton 2002

- Contrastive divergence learning, Hinton 2002
음성 인식의 발전
- 1980년대의 hidden markov 모델이 현재에도 time-series sequence에서도 적용이 비교적 효과적인 모델 중 하나이다.
- Deep neural network의 도입에 따라 guassian distribution 모델을 대체하여, DNN(RNN + LSTM)이 큰 성능의 향상을 가져왔다.
3. 자연언어처리에서의 Deep learning - 권혁철 : 부산대학교
자연언어처리의 4대 요소기술
- 형태소 분석 Morphological segmentation
- 통사 분석 Syntactic analysis
- 의미 분석 Semantic analysis
- 어려움 : 어의 중의성 word sense disambiguation
- 화용 분석 Pragmatic Analysis
자연언어처리 응용기술
- 기계번역 (machine translation)
- 정보검색 (information search)
- 질의응답 (query retrieval)
- 음성인식 (speech recognition)
- 음성합성 (speech composition)
- 문서축약
- 맞춤법/문법 검사
Tutorials
Tensorflow Ex3.Linear Regression
Useful links
TensorFlow tutorials
TensorFlow basic usages
Artificial Neural Network : Wikipedia
The neural networks behind Google Voice transcription
